rheumatoid spine
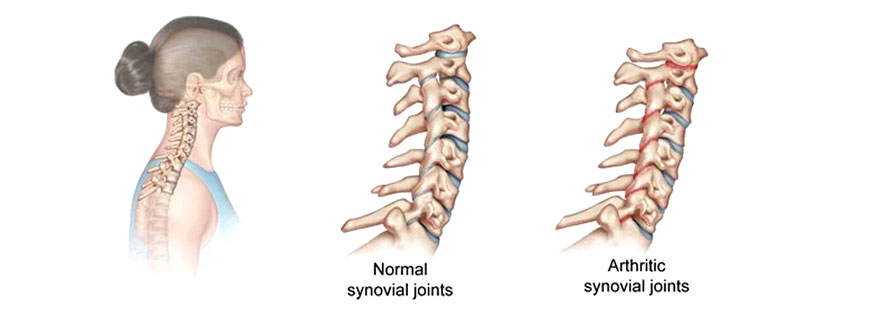
Rheumatoid spine refers to the involvement of the spine in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints. While RA commonly affects the small joints of the hands and feet, it can also impact the spine, leading to various complications.
Here's an overview of rheumatoid spine:
- Pathophysiology: Rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by chronic inflammation of the synovial lining of joints, which can lead to joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and progressive joint damage. In the spine, RA primarily affects the cervical spine (neck) and can involve the facet joints, atlantoaxial joint, and intervertebral discs.
- Symptoms:
- Neck pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion
- Radiating pain or numbness into the arms or hands
- Weakness or difficulty with fine motor tasks
- Instability or difficulty maintaining balance
- Symptoms of spinal cord compression, such as difficulty walking, loss of bowel or bladder control, or sensory changes
- Prognosis: The prognosis for rheumatoid spine depends on factors such as the severity and extent of spinal involvement, the effectiveness of treatment, and the presence of neurological complications. While treatment can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression, individuals with rheumatoid spine may still experience long-term complications such as chronic pain, disability, and neurological deficits.