lumbar vertebrae fusion
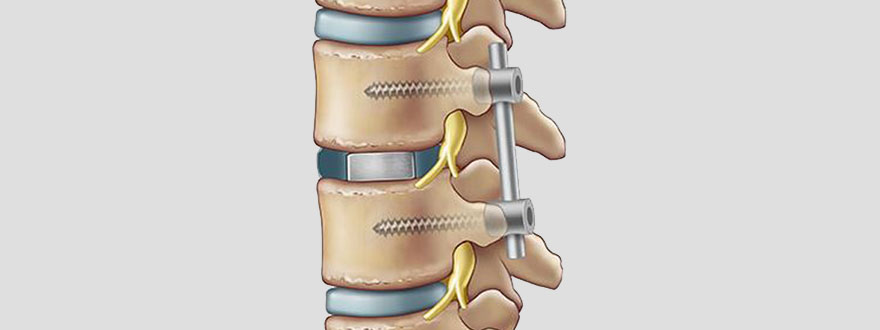
Lumbar vertebral fusion, also known simply as spinal fusion, is a surgical procedure performed to stabilize the spine and alleviate symptoms caused by various spinal conditions. It involves joining together two or more vertebrae in the lumbar (lower back) region to form a single, solid bone. This fusion prevents movement between the fused vertebrae, thereby reducing pain and providing stability to the spine.
Here's an overview of lumbar vertebral fusion:
- Indications: Lumbar vertebral fusion is commonly performed to treat a range of spinal disorders, including:
- Degenerative disc disease: Wear and tear on the spinal discs, leading to disc herniation, instability, and nerve compression.
- Spinal stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal, which can compress the spinal cord or nerve roots and cause pain, numbness, or weakness in the legs.
- Spondylolisthesis: Forward displacement of one vertebra over another, often causing spinal instability and nerve compression.
- Spinal fractures: Fractures or instability of the vertebrae due to trauma or other spinal injuries.
- Bone Grafting: Bone grafting is a crucial component of lumbar vertebral fusion, as it promotes the formation of new bone between the fused vertebrae. Bone graft material may be obtained from the patient's own body (autograft) or from a donor (allograft). In some cases, synthetic bone graft substitutes or bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) may also be used to facilitate fusion.
- Implants and Instrumentation: Metal implants such as screws, rods, and cages are often used to provide stability and support during the fusion process. These implants help maintain proper alignment of the spine and facilitate the integration of the bone graft. The choice of implants and instrumentation depends on factors such as the patient's anatomy, the extent of spinal pathology, and the surgeon's preference.
- Outcomes: Lumbar vertebral fusion can provide significant relief of symptoms and improve spinal stability for many patients.