Arthroscopy
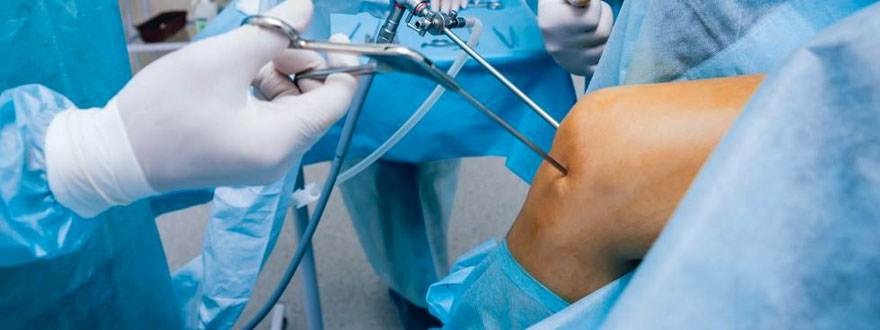
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat a variety of joint-related conditions. It involves the insertion of a small, flexible instrument called an arthroscope into the joint through tiny incisions. The arthroscope is equipped with a camera that provides a magnified view of the joint's interior on a monitor, allowing the surgeon to visualize the structures within the joint in real time.
Here's an overview of arthroscopy:
- Diagnosis: Arthroscopy allows for direct visualization of the inside of a joint, enabling the surgeon to assess and diagnose various joint conditions, such as tears in ligaments, cartilage damage, inflammation, or loose bodies (fragments of bone or cartilage).
- Advantages:
- Minimally Invasive: Arthroscopy involves smaller incisions compared to traditional open surgery, resulting in less tissue damage, reduced scarring, and faster recovery times.
- Accurate Diagnosis: Direct visualization of the joint allows for accurate diagnosis of various joint conditions, leading to more targeted and effective treatment.
- Reduced Complications: The minimally invasive nature of arthroscopy typically results in fewer complications such as infection, blood loss, and postoperative pain compared to open surgery.
- Indications: Arthroscopy can be performed on various joints, including the knee, shoulder, hip, ankle, elbow, and wrist, depending on the specific condition being treated. Common indications for arthroscopy include meniscal tears, ligament injuries (e.g., ACL tears), rotator cuff tears, cartilage damage, synovitis, loose bodies, and impingement syndromes.